What is basic daydreams on Android? This exploration dives into the fascinating world of Android’s hidden potential, revealing how these seemingly simple features can unlock powerful experiences. Imagine a background application that subtly enhances your device’s functionality, subtly adjusting and improving your daily interactions. Understanding the basics is key to unlocking this potential.
Daydreams, in their most basic form, are background processes that run on Android devices. They are designed to perform specific tasks without requiring direct user input. This allows for optimized resource management and efficient background operations. This document will break down the concept, guiding you through development and implementation. From creating simple prototypes to advanced functionalities, this comprehensive guide provides actionable insights into developing and implementing this unique Android feature.
Introduction to Basic Daydreams on Android
Basic daydreams on Android are a fascinating feature, subtly enhancing the user experience without demanding significant attention. They represent a powerful tool for background tasks, offering a low-power approach to performing essential actions while the device is idle. Imagine background updates happening seamlessly, without interrupting your work or entertainment, all thanks to these ingenious tools.These background tasks are carefully managed, ensuring they don’t drain your battery or overload your processor.
They work in harmony with other Android features, enabling a smooth and efficient operation. This sophisticated design makes them crucial for the overall functionality of Android devices.
Fundamental Components of Basic Daydreams
Daydreams are built upon a foundation of specific components, each playing a crucial role in their operation. These components work together to achieve the intended functionality. The key elements include:
- Scheduling Mechanism: This mechanism ensures that daydreams are activated at appropriate intervals, without interfering with the foreground application or user experience. It’s designed to minimize impact on system performance.
- Task Execution: This aspect focuses on the actual work done by the daydream. It includes handling data updates, background computations, and interacting with other system services. The task execution is optimized to be quick and efficient.
- Resource Management: Daydreams must adhere to strict resource constraints. This includes limitations on CPU usage, memory allocation, and network access. These limitations are essential for preventing the daydream from becoming a performance bottleneck.
Role of Basic Daydreams in the Android Ecosystem
Basic daydreams are integral to the Android ecosystem. They contribute to the system’s responsiveness and efficiency, improving user experience. They ensure that background processes run smoothly, without interfering with foreground tasks or impacting battery life. By handling certain operations discreetly, daydreams contribute to a smoother, more seamless user experience.
Typical Use Cases for Basic Daydreams on Android
Daydreams offer a diverse range of applications in Android. They can be used for a multitude of purposes, all contributing to the efficiency of the device. Some common use cases include:
- Background Data Updates: Daydreams can fetch and process data from various sources, like weather updates, news feeds, or social media notifications. This allows for continuous updates without interrupting the user’s current activity.
- Content Synchronization: Daydreams can perform tasks such as syncing data between applications or devices. This synchronization ensures that data is always up-to-date.
- Image or Video Processing: Daydreams can be utilized to perform image or video processing tasks, such as image optimization or video encoding. This can be essential for improving the performance of media applications.
Comparison to Other Android Features
The following table compares basic daydreams to other common Android features, highlighting their distinct characteristics and functions.
| Feature | Basic Daydreams | Widgets | Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Background tasks, low-power operations | Visual displays, interactive elements | Long-running processes |
| Execution | Discrete, scheduled, low-priority | Continuous, interactive, foreground | Continuous, background, potentially high-priority |
| Resource Usage | Minimized | Moderate | Variable |
| User Interaction | None | Direct | Indirect (often through other apps) |
Developing Basic Daydreams
Crafting a simple yet engaging daydream app on Android opens doors to a world of interactive experiences. This journey will detail the steps to build such an app, from initial design to user interaction, and highlight the crucial elements for success. It delves into the necessary APIs and libraries, illustrating their integration and providing a clear roadmap for your project.This exploration of developing basic daydreams on Android will equip you with a practical understanding of the core components involved.
The emphasis will be on creating a functional app, laying a solid foundation for future enhancements and extensions. The key is to break down the process into manageable steps, focusing on clarity and practical application.
Designing the App Structure
A well-structured daydream app ensures a seamless user experience. This involves careful planning of the screens, functionalities, and user interactions. The structure should prioritize intuitive navigation and a visually appealing interface. Consider the user flow, from initial launch to engaging with the core features.
Choosing the Essential APIs and Libraries
Several APIs and libraries form the bedrock of any Android development project. For daydreams, core components like the `View` system for rendering elements, `Activity` lifecycle for handling app states, and `InputMethodManager` for managing user input are essential. These fundamental building blocks ensure the app’s core functionality and responsiveness. Also, consider libraries like `ConstraintLayout` for layout management and `Material Design` for a polished aesthetic.
Integrating with Other Android Features
A daydream app isn’t isolated; it interacts with the broader Android ecosystem. Integrating with features like the system’s notification system allows you to update the user on progress or provide relevant information. This seamless integration enhances the overall user experience and functionality. For example, integrating with the user’s calendar can create reminders or trigger specific daydreams based on events.
Handling User Interactions
User interaction is the heart of any daydream application. Designing intuitive controls, such as buttons, sliders, or text input fields, is crucial. Listeners for user events (like button clicks) are fundamental for triggering specific actions or animations within the daydream. Implementing robust input handling and validation ensures a smooth user experience.
Comparing Approaches to Building Basic Daydreams
| Approach | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Using Fragments | Modular approach, breaking down the UI into reusable components. | Improved code organization, reusability, testability. | Potential for complexity in more intricate apps. |
| Employing Activities | Traditional Android UI building method. | Simplicity for basic structures. | Can lead to tightly coupled code, harder to maintain in complex apps. |
| Utilizing a View-Model Architecture | Decouples UI from data management logic, leading to cleaner, testable code. | Improved maintainability, scalability, and testability. | Requires understanding and setup of a more complex structure. |
A table summarizing the key aspects of different approaches helps in making informed decisions. Choosing the right approach depends on the app’s complexity and scalability requirements.
Implementing User Interface (UI) in Basic Daydreams: What Is Basic Daydreams On Android
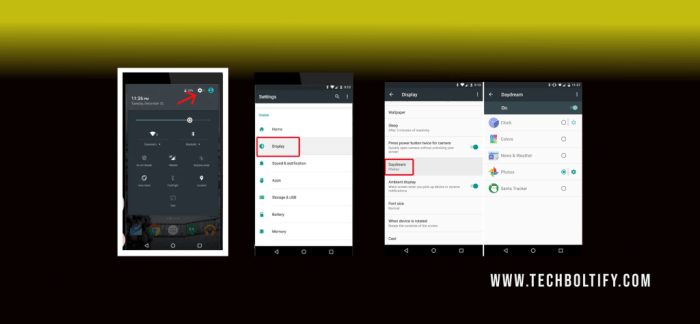
Crafting a captivating user interface (UI) is key to making your Basic Daydream app truly shine. Think of it as the stage for your app’s story – a visually appealing and intuitive space where users can effortlessly navigate and engage. This section dives into the specifics of designing a compelling UI, tailored to the unique constraints of Daydream’s immersive environment.Designing a UI for Daydreams requires a mindful approach, balancing visual appeal with the limited screen real estate.
Daydreams aren’t about cluttered interfaces; they’re about seamless, intuitive interactions. Effective UI design for these experiences means making every element count.
Designing for Limited Screen Space
Daydream’s unique focus on immersive experiences necessitates careful consideration of the screen’s limitations. A well-designed UI should prioritize clear visual hierarchy and intuitive navigation. Visual elements should be easily discernible at a glance, even from a distance. Think about the user’s perspective and the optimal viewing angle.
Using Visual Effects to Enhance User Experience, What is basic daydreams on android
Visual effects are crucial for enhancing immersion and guiding the user through the experience. Strategic use of subtle animations and transitions can create a sense of depth and movement, without distracting from the core experience. Avoid overwhelming the user with excessive effects; keep them refined and purposeful.
Utilizing Animations in Daydreams
Animations can significantly enhance the user experience in a Basic Daydream. A smooth transition from one screen to another, or a subtle animation of an object, can communicate information effectively and engage users. Animations should complement the experience, not overshadow it. For example, a subtle fade-in/fade-out effect for menu items adds visual flair without being distracting.
Examples of Effective Animation Use
Imagine a loading screen that subtly rotates a 3D model of the app’s logo. Or, consider a game where a character’s movements are accompanied by a gentle ripple effect in the surrounding environment. These examples illustrate how animations can add depth and interest to a Daydream experience.
UI Design Patterns for Basic Daydreams
This table showcases various UI design patterns that can be applied to Basic Daydreams, highlighting their potential applications and key characteristics:
| Design Pattern | Description | Application | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Floating Panels | Overlays that appear on top of the scene | Displaying information or controls | Intuitive, easily accessible, adjustable size |
| Gesture-Based Interactions | Controls that respond to user hand movements | Navigation, selection, manipulation | Immersive, natural, responsive |
| Interactive 3D Objects | Objects within the scene that respond to user interaction | Menus, buttons, controls | Dynamic, visually engaging, immersive |
| Layered Interface | UI elements that appear and disappear in layers | Showing additional details or options | Clear visual hierarchy, easily adjustable, focused display |
Performance Considerations in Basic Daydreams

Crafting a smooth and responsive Daydream experience is crucial for user engagement. Ignoring performance optimization can lead to a frustrating and ultimately unsuccessful application. This section delves into the vital aspects of performance tuning for basic Daydream implementations.Optimizing performance isn’t just about speed; it’s about creating an experience that feels effortless and seamless. A laggy or unresponsive Daydream app can quickly deter users, regardless of how innovative the core concept may be.
This section will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to build high-performing Daydream applications.
Potential Performance Bottlenecks
Several factors can hinder the performance of basic Daydream applications. Inefficient rendering of 3D models, heavy use of CPU resources, and excessive memory allocation can all contribute to a sluggish user experience. Overuse of complex animations or poorly optimized graphics can severely impact the responsiveness of the app. Furthermore, background processes or unmanaged threads can significantly degrade performance.
Minimizing Resource Consumption
Efficient resource management is key to a smooth Daydream experience. Using optimized 3D models and textures, along with carefully crafted animation sequences, can dramatically reduce the load on the device’s GPU. Implement efficient data structures and algorithms to minimize memory usage. Leveraging hardware acceleration for computationally intensive tasks can also significantly improve performance. By carefully analyzing and reducing the number of computations, the application’s resource footprint can be drastically reduced.
Improving Responsiveness
Responsiveness in Daydream applications is critical. Users expect immediate reactions to their actions. Optimize UI elements for quick rendering and efficient interaction. Use asynchronous operations for tasks that might take a noticeable amount of time to complete, like fetching data or performing complex calculations. Avoid blocking the main thread with lengthy operations.
Methods for Optimizing Performance
Implementing these techniques will improve your application’s performance.
| Optimization Strategy | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Optimized 3D Models | Reduce polygon count and complexity to reduce rendering time. | Using simpler shapes and fewer details. |
| Efficient Data Structures | Choose appropriate data structures for storing and accessing data to avoid memory leaks and unnecessary computations. | Using a hash table instead of a linear search when searching for elements. |
| Asynchronous Operations | Offload time-consuming tasks to separate threads or background processes. | Fetching data from a network in the background while the UI remains responsive. |
| Hardware Acceleration | Use OpenGL ES or other hardware-accelerated APIs for graphics and rendering. | Using OpenGL ES for rendering instead of software-based rendering. |
| Memory Management | Explicitly manage memory allocation and deallocation to avoid memory leaks. | Using a garbage collector or manually freeing unused objects. |
Data Handling and Persistence in Basic Daydreams
Managing data within a basic Daydream experience is crucial for a smooth and engaging user experience. Efficient storage and retrieval of information directly impact responsiveness and overall application quality. From simple settings to complex interactions, data persistence allows for remembering user choices and progress across sessions.Data handling involves more than just storing values; it encompasses choosing the right data structures for optimal performance and considering how to keep data safe and accessible throughout the app’s lifecycle.
Understanding the different data storage options, their strengths, and limitations is key to building a robust and user-friendly Daydream application. The strategies for persistence and retrieval directly influence the user’s experience and must be carefully planned.
Methods for Handling Data
Choosing the right data structure is paramount for efficient data management. For simple data, like user preferences, key-value stores are an excellent choice. More complex data, such as user profiles or game progress, might benefit from relational databases or object-oriented data models. Selecting the appropriate structure ensures that data retrieval and manipulation are optimized for the application’s specific needs.
Strategies for Storing and Retrieving Data
Effective storage and retrieval strategies are essential for a responsive and engaging Daydream experience. Data persistence ensures that user choices and application state are preserved between sessions. Implementing local storage solutions, like SharedPreferences, is often sufficient for basic Daydreams, but more complex data structures may require external storage mechanisms.
Appropriate Data Structures for Efficient Data Management
For basic Daydreams, key-value stores are often sufficient for simple data like user preferences or settings. However, for larger datasets or more complex data structures, consider relational databases or object-oriented models. These more robust solutions can handle more intricate data relationships and provide better scalability for future expansions.
Implementing Data Persistence in Basic Daydreams
Implementing data persistence involves choosing a storage mechanism and writing code to save and retrieve data. For basic Daydreams, utilizing Android’s SharedPreferences is a straightforward approach. For larger datasets or more complex requirements, exploring external storage solutions like SQLite databases or cloud storage might be necessary. Each method has advantages and disadvantages, and the best approach will depend on the specific needs of your application.
Comparison of Data Storage Options
| Storage Option | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| SharedPreferences | Simple key-value store for basic data. | Easy to use, fast retrieval for small datasets. | Limited to simple key-value pairs, not suitable for complex data structures. |
| SQLite Database | Relational database for structured data. | Handles complex data relationships, scalable for larger datasets. | More complex to implement than SharedPreferences, requires SQL knowledge. |
| Cloud Storage (e.g., Firebase Realtime Database) | Data stored on a remote server. | Enables data synchronization across devices, real-time updates. | Requires network connection, potential security concerns. |
Advanced Concepts in Basic Daydreams
Basic Daydreams, while offering a solid foundation, can be significantly enhanced by incorporating more complex functionalities. This exploration delves into extending these foundational concepts, incorporating external resources, and integrating with other applications for a richer and more dynamic user experience. Imagine a Daydream that not only displays information but also interacts seamlessly with your existing apps and services – this is the potential we unlock.
Extending Functionality with Complex Features
Basic Daydreams often focus on static displays. Advanced implementations allow for dynamic content updates, user interactions beyond simple taps, and more intricate animations. For example, a daydream could respond to user gestures, displaying different content based on their movements. This could range from a simple change in visual elements to more complex interactions like controlling a virtual object with head movements.
Further, integrating interactive elements like buttons, sliders, or even mini-games will make the experience far more engaging.
Incorporating External Services and APIs
Connecting Daydreams to external services opens up a world of possibilities. Imagine a Daydream that displays real-time weather information, traffic updates, or even stock quotes. This is achieved through API integration. The key here is selecting the right APIs. This involves researching suitable APIs, understanding their data structures, and implementing secure and efficient methods for data retrieval.
Proper error handling and rate limiting are crucial to ensure the stability and responsiveness of the Daydream. Real-world examples include integrating social media feeds, displaying live maps, or using weather APIs for dynamic display.
Integration with Other Apps and Systems
Daydreams aren’t isolated entities. Advanced designs enable seamless integration with other applications and systems. Imagine a Daydream that automatically displays relevant information from another app when a particular event occurs. This could be a calendar event, a notification, or a specific file. Such integration necessitates careful design to ensure the Daydream doesn’t disrupt the workflow of the primary application.
Furthermore, it involves understanding the data formats and communication protocols between the systems, as well as handling security considerations. Examples could be displaying relevant documents from a productivity app within the Daydream or receiving updates from a health tracking application.
Advanced UI Interactions
Enhancing user experience hinges on intuitive and responsive UI interactions. Beyond simple taps and gestures, advanced Daydreams can incorporate features like haptic feedback, voice commands, and even eye-tracking. This enables a more immersive and natural interaction with the virtual environment. Implementing these features requires a deep understanding of the underlying Android APIs and user-centered design principles. Think about Daydreams that respond to voice commands to adjust settings, change content, or trigger actions, or those using haptic feedback to provide a more physical presence in the virtual environment.
Comparing Basic and Advanced Daydreams
| Feature | Basic Daydreams | Advanced Daydreams |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Static displays, limited interactions | Dynamic content, complex interactions, animations |
| External Services | No external service integration | Integration with external APIs for data retrieval |
| App Integration | No integration with other apps | Seamless integration with other apps and systems |
| UI Interactions | Simple taps and gestures | Haptic feedback, voice commands, eye-tracking |
| Complexity | Simple | Complex |
Illustrative Examples of Basic Daydreams

Daydreams, those fleeting wanderings of the mind, can take many forms, even in the digital realm. Basic Daydreams on Android, with their focus on simplicity and intuitive interaction, offer a captivating window into this mental landscape. Let’s explore some concrete examples, examining their functionalities, interfaces, design choices, and ultimately, their impact.
Real-World Basic Daydream Examples
Basic Daydreams, by their nature, aim for a straightforward and user-friendly experience. This translates to a variety of potential applications, all designed with ease of use and intuitive interactions in mind. Consider a simple weather app that, rather than just displaying a forecast, overlays a 3D model of clouds and precipitation onto the live camera feed, providing a dynamic, immersive experience.
Or imagine a relaxation app that subtly shifts ambient lighting and sound cues based on your chosen activity, creating a personalized and immersive atmosphere. These examples, while basic in concept, showcase the potential for creativity and engagement within a Daydream framework.
Functionalities and User Interfaces
Different implementations will naturally vary in their specific functionalities. A simple to-do list app might leverage Daydream’s spatial capabilities to display tasks floating in the air, easily navigable with hand gestures. Alternatively, a guided meditation app could use Daydream’s depth perception to display animated visualizations alongside calming soundscapes. The user interface, then, would be crucial in conveying the app’s function in a way that is both understandable and engaging.
Imagine a simple, minimalist design, perhaps with large, easily-selectable icons for different functions.
Design Considerations and Development Processes
Careful consideration of the user experience is paramount. The layout of the UI, the responsiveness of the application, and the overall intuitiveness of the interaction are crucial factors. Developers need to consider how the user will interact with the application and anticipate potential issues. Think about the flow of information and how the interface adapts to different screen sizes and user preferences.
For example, a well-designed to-do list app would allow users to easily add, delete, and prioritize tasks within the Daydream environment. A guided meditation app would be carefully crafted to ensure seamless transitions between different phases of the meditation.
Benefits and Limitations
Basic Daydream apps, due to their nature, offer several advantages. They provide an immersive and engaging experience, especially when used for relaxation, learning, or productivity. However, they also have limitations. Processing power and memory constraints might hinder the creation of more complex visual experiences. A well-optimized app would be able to handle these limitations effectively, while a less optimized app could suffer from performance issues.
Illustrative Table of Basic Daydream Apps
| App Category | Functionality | UI Description | Design Considerations | Screenshot/Visual Representation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weather App | Displays a 3D model of clouds and precipitation overlaid on a live camera feed. | Simple, minimal interface with large, easily selectable icons. | Smooth rendering of the 3D model, minimal lag in updating the display. | Imagine a live view of the user’s surroundings with clouds and rain visibly overlaying. |
| To-Do List | Allows users to add, delete, and prioritize tasks using hand gestures. | Tasks displayed as floating objects in 3D space. | Intuitive gesture controls, clear visual feedback. | Imagine floating to-do list items interacting with the user’s hands. |
| Guided Meditation | Provides guided meditations with animated visualizations and sound cues. | Dynamic visualizations and sound cues adapting to the meditation phase. | Seamless transitions between different phases of the meditation, clear feedback. | Imagine abstract shapes and colors changing dynamically during the meditation process. |
