Anycast como conectar Android: Descubre cómo aprovechar la tecnología Anycast para conectar tus dispositivos Android a servicios distribuidos de manera eficiente y segura. Esta guía te mostrará cómo funciona Anycast, cómo se integra con Android, los pasos para configurar la conexión, las posibles fallas y soluciones, y las consideraciones de seguridad. Prepárate para un viaje a través del mundo de las conexiones distribuidas y las aplicaciones de Android.
En la era de la conectividad global, la tecnología Anycast emerge como una solución poderosa para conectar dispositivos Android con servicios en todo el mundo. Imagine una red donde la respuesta a su solicitud se encuentra en el servidor más cercano, independientemente de la ubicación física del servidor. Anycast permite precisamente esto, mejorando la velocidad y la confiabilidad de las conexiones, algo crucial para aplicaciones modernas que necesitan acceso a datos en tiempo real y desde cualquier lugar.
Anycast and Android Devices
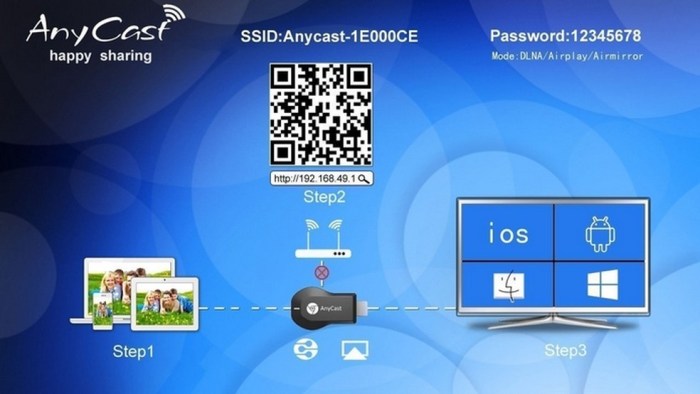
Anycast, a powerful networking technique, offers significant potential for enhancing Android applications and devices. Its ability to distribute traffic across multiple servers improves performance and reliability. This adaptability aligns well with the dynamic nature of Android’s ecosystem, from personal devices to enterprise deployments.Anycast’s versatility makes it a compelling choice for applications requiring high availability and low latency. Its distributed nature allows for rapid response times, crucial for applications demanding real-time interaction or requiring seamless access from various geographical locations.
By leveraging Anycast, Android devices can benefit from a more robust and responsive network experience.
Leveraging Anycast in Android Applications
Anycast, in its essence, is a clever way to route traffic to the nearest server. This strategic placement is key to improving user experience. By deploying servers in various locations, Anycast allows Android applications to connect to the closest available server. This results in faster response times and reduced latency.
Technical Integration of Anycast Routing
Integrating Anycast into Android’s network stack requires careful consideration of the existing networking protocols. The Android framework already has mechanisms for handling network connectivity, but adapting it to leverage Anycast involves modifications to handle the distributed server infrastructure. This might entail custom routing protocols or specialized network libraries tailored to the Anycast architecture. The specifics would depend on the nature of the application and the desired level of Anycast integration.
Examples of Benefiting Applications
Android applications heavily reliant on real-time data, such as gaming applications or video streaming platforms, can significantly benefit from Anycast connectivity. Real-time multiplayer games benefit from low latency, allowing for smoother gameplay. Streaming services can maintain consistent playback speed and minimize buffering. Furthermore, location-aware applications could leverage Anycast to direct users to the closest server, enhancing responsiveness and reducing data transfer time.
Potential Use Cases and Their Implications
| Use Case | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time Multiplayer Gaming | Reduced latency, smoother gameplay, improved responsiveness across diverse geographical locations. | Ensuring consistent performance across all servers, managing the dynamic distribution of players to the closest servers. |
| Video Streaming Services | Improved streaming quality, reduced buffering, enhanced user experience by minimizing latency. | Maintaining consistent video quality and playback speed across geographically distributed viewers, managing server load and bandwidth. |
| Location-Based Services | Faster response times, reduced data transfer time, enhanced responsiveness, enabling precise location data access. | Managing the distribution of requests to the nearest server, ensuring reliable and consistent location data. |
| Cloud Storage and File Sharing | Enhanced speed and reliability of file access, minimizing download times, improving user experience. | Ensuring consistent file access and availability from different geographical locations, maintaining data integrity and security. |
Connecting Android to Anycast Services
Unlocking the potential of Anycast services on your Android device is a straightforward process. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the connection procedure, ensuring a seamless experience for all users. From initial setup to successful streaming, we’ll cover everything you need to know.Understanding the fundamental principles of Anycast connectivity is key to leveraging its capabilities. Anycast, in essence, distributes content across multiple servers, providing high availability and fast response times.
Android devices, with their versatile nature, are perfectly suited to tap into this network.
Connection Steps
The connection process involves several key steps, each contributing to a smooth and reliable connection. Begin by ensuring your Android device is appropriately configured and ready to receive the Anycast stream.
- Verify network connectivity. A stable Wi-Fi or mobile data connection is essential for successful Anycast streaming.
- Locate the Anycast service’s IP address or hostname. This information is crucial for establishing the connection.
- Initiate the connection process within the Android device’s settings. This might involve selecting the service or entering the required details.
- Authenticate, if required. Some Anycast services require authentication for access, which often involves entering a username and password.
Protocols for Anycast Connectivity
Different protocols facilitate communication between Android devices and Anycast services. Each protocol has its own strengths and weaknesses, influencing the overall experience.
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a connectionless protocol, making it ideal for applications demanding low latency, such as streaming media. Its lightweight nature is well-suited for the high-bandwidth demands of Anycast services.
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a connection-oriented protocol, ensuring reliable data transmission. While it might introduce a slight delay compared to UDP, its reliability is often a priority for critical data exchange.
Configuration for Connecting to an Anycast Service
Specific configurations are essential for establishing a robust connection. A well-configured Android device is critical for smooth and uninterrupted service.
- Configure the network settings on the Android device. Ensure the correct network configuration, such as IP address and port number, is properly set up.
- Enter the service’s specific credentials. These may include an API key or similar authentication parameters required by the Anycast service.
- Verify the device’s compatibility. Certain Android versions or device models might have specific compatibility issues with certain Anycast services.
Connection Flowchart
The following flowchart visually demonstrates the connection process from request to establishment:“`[Visual Flowchart](Start) –> [Check Network Connectivity] –> [Obtain Service Details] –> [Initiate Connection] –> [Authentication (if required)] –> [Establish Connection] –> (Success)“`Note: A visual flowchart would illustrate the steps more clearly. This description serves as a textual representation.
Configuration and Troubleshooting: Anycast Como Conectar Android
Connecting your Android device to Anycast services should be a breeze. This section provides a step-by-step guide to ensure a seamless connection and resolves common pitfalls. Troubleshooting is key to getting the most out of your Anycast experience.Navigating the configuration process and understanding potential problems is crucial for a smooth Anycast experience. This section meticulously details the configuration process and common hurdles.
It will also Artikel how to identify and fix network connectivity issues.
Configuring Android Devices for Anycast
To establish a successful connection, your Android device needs to be correctly configured. Follow these steps:
- Ensure your Android device and the Anycast service are on the same Wi-Fi network.
- Launch the Anycast application on your Android device.
- Select the desired Anycast service from the list of available devices.
- The connection should be established automatically. If not, verify that the service’s Wi-Fi credentials are correct.
- If the connection fails, review the network settings on both your Android device and the Anycast service.
Common Connection Issues and Troubleshooting
Various factors can hinder a successful connection. This section addresses typical issues and their solutions.
- Incorrect Wi-Fi Credentials: Double-check the Wi-Fi password for both your device and the Anycast service. Typographical errors are a common culprit. Ensure the service is connected to the correct network and the password matches.
- Network Interference: Other devices or applications on the network might be interfering. Try turning off or restarting other devices or applications on the network to rule out this potential cause.
- Firewall Restrictions: Firewall settings on your device or router could be blocking the Anycast service. Adjust firewall settings to allow Anycast communication. This typically involves opening ports used by the Anycast service.
- Outdated Anycast Application: An outdated application might not be compatible with the current service. Check for updates in the app store.
- Device Compatibility Issues: Some devices may not be compatible with the current Anycast service version. Verify device compatibility and update the Anycast application.
Diagnosing Network Connectivity Problems
Network connectivity issues can stem from various sources. Here’s how to pinpoint the problem:
- Check Wi-Fi Signal Strength: A weak signal can lead to connection problems. Ensure your device has a strong and stable Wi-Fi signal.
- Test Network Speed: Slow network speeds can hinder connection stability. Test your network speed to determine if it’s adequate for the Anycast service.
- Restart Network Devices: Restarting your router and modem can resolve temporary network glitches.
- Check for Other Network Issues: Other devices or applications on the network might be causing problems. If possible, isolate your Android device on a separate network.
Common Anycast Connection Errors and Solutions
This table Artikels common connection errors and their solutions.
| Error | Solution |
|---|---|
| Connection Timed Out | Verify network connectivity, restart the Anycast service, or try a different Wi-Fi network. |
| Invalid Credentials | Double-check Wi-Fi passwords for both your device and the Anycast service. |
| Service Unavailable | Contact Anycast support for assistance. |
| Network Error | Restart your router, modem, and/or device. Verify network settings. |
Security Considerations for Android Anycast
Navigating the digital landscape demands a keen awareness of potential security risks, especially when dealing with technologies like Anycast. Connecting Android devices to Anycast services opens exciting possibilities, but also necessitates careful consideration of security implications. This section delves into the vulnerabilities and strategies for safeguarding your Android devices in the Anycast ecosystem.Anycast, by its very nature, distributes network traffic across multiple servers.
While this enhances speed and reliability, it can also introduce complexity into the security equation. This necessitates a multi-layered approach to ensure secure communication and data protection. Understanding the potential vulnerabilities allows for proactive measures to mitigate risks and maintain the integrity of your Android devices’ interactions with Anycast services.
Potential Vulnerabilities and Risks
Anycast systems, though robust, are susceptible to a range of security threats. Compromised servers or malicious actors intercepting data in transit are potential hazards. Poorly configured Android devices or applications can expose vulnerabilities that hackers could exploit. In addition, the sheer volume of data transmitted across the Anycast network could become a target for malicious actors.
Security Measures for Android Devices, Anycast como conectar android
Implementing robust security measures is crucial for mitigating risks. Ensure that the Android devices used with Anycast services are regularly updated with the latest security patches. This proactive approach helps to close known vulnerabilities. Strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regularly updated apps are also critical safeguards. Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for Anycast connections adds an extra layer of security, encrypting the communication channel.
Security Protocols and Best Practices
Implementing strong security protocols and adhering to best practices are paramount for secure Anycast connections. Use Transport Layer Security (TLS) or similar encryption protocols for all data transmissions. This ensures that data exchanged between your Android device and Anycast servers remains confidential. Regularly reviewing and updating security settings on your Android devices is also crucial. The use of robust firewall configurations can also help in preventing unauthorized access.
Example of a Secure Anycast Setup
Consider an Android-based point-of-sale system connected to an Anycast payment gateway. By employing TLS encryption, the financial transactions are protected from eavesdropping. Additionally, strong authentication methods, like multi-factor authentication, ensure that only authorized users can access the system. Regular security audits and vulnerability scans of the Android devices and the Anycast system are vital to proactively identify and address any potential weaknesses.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-world applications of Anycast technology on Android devices are flourishing, showcasing significant performance gains and innovative functionalities. These examples highlight the versatility and power of Anycast in transforming how Android apps interact with distributed resources. From gaming to streaming, the potential applications are vast.
Real-World Applications
Anycast’s ability to dynamically route traffic across multiple servers allows for seamless scalability and enhanced performance in demanding applications. This dynamic nature enables applications to leverage the strengths of distributed systems, handling spikes in user demand effectively and consistently. A notable example is the integration of Anycast into live-streaming apps.
- Live streaming platforms can utilize Anycast to deliver content to users based on their geographical location, ensuring low latency and high-quality playback. This is particularly crucial for users in regions with high network congestion. The system intelligently directs the stream to the nearest server, reducing delays and improving the overall user experience.
- In gaming, Anycast can be employed to distribute game data and resources to various servers across the globe, enabling global play without performance issues. This approach allows players in different time zones to participate in multiplayer games, minimizing lag and ensuring a consistent gameplay experience. The servers are dynamically selected based on player location, providing the fastest possible connection.
- Content delivery networks (CDNs) often utilize Anycast to distribute media files and applications, ensuring fast access to content for users around the world. This is evident in popular video-sharing platforms where Anycast is instrumental in delivering high-quality video to users worldwide, regardless of their network location.
Implementation Details
Integrating Anycast into an Android application involves several key steps. These include selecting the appropriate Anycast service provider, configuring the application to utilize the service, and developing the logic to handle the dynamic routing of requests. Proper configuration is critical to achieving the performance benefits of Anycast.
- Selecting the service provider is a crucial first step. Factors such as pricing, reliability, and available features should be considered.
- The Android application’s code needs to be modified to utilize the Anycast API. This involves integrating the API calls into the application’s logic, enabling the application to direct requests to the appropriate server.
- Handling dynamic routing is essential for optimal performance. The application must be programmed to detect the user’s location and choose the closest server dynamically.
Performance Benefits and Challenges
The use of Anycast significantly improves application performance by minimizing latency and improving overall user experience. Reduced latency is particularly beneficial for applications relying on real-time data or streaming, enhancing user engagement.
- Improved latency is the primary benefit of Anycast, leading to faster loading times and smoother streaming.
- Increased scalability is another significant advantage, enabling the application to handle more users without sacrificing performance.
- Potential challenges include managing the complexity of integrating Anycast into the application and ensuring reliability across multiple servers.
Case Study: A Streaming Music App
A hypothetical streaming music app, “GlobalMelodies,” integrates Anycast for enhanced performance and global reach. The app utilizes a network of geographically distributed servers, each containing a portion of the music library.
| Feature | Implementation Detail |
|---|---|
| Content Distribution | Anycast dynamically routes music requests to the nearest server, ensuring low latency and high-quality playback. |
| User Experience | Users experience seamless playback, regardless of their location. |
| Scalability | The system can easily scale to accommodate a large number of users without impacting performance. |
“Anycast significantly reduced latency for users in remote locations, improving their listening experience.”
Future Trends and Developments

The world of Anycast is rapidly evolving, promising exciting possibilities for Android users. We’re moving beyond the basics, envisioning a future where Anycast seamlessly integrates into our daily lives, offering unparalleled convenience and potential. This exploration delves into emerging trends, potential applications, and the profound impact Anycast will have on mobile computing.Anycast, initially designed for efficient content delivery, is now poised to redefine how we interact with information and services on our Android devices.
Imagine a future where location-agnostic access to resources becomes the norm, driven by Anycast’s intelligent routing capabilities. This transformation is likely to lead to a more interconnected and responsive mobile experience.
Emerging Trends in Anycast Technology
Anycast technology is constantly being refined and expanded. We’re seeing advancements in real-time traffic analysis, enabling more dynamic routing and optimized resource allocation. This leads to reduced latency and enhanced user experience, especially crucial for applications demanding high responsiveness, such as live streaming and gaming. Furthermore, the integration of AI into Anycast systems promises to anticipate user needs and optimize delivery even further.
Potential Future Applications of Anycast on Android
Anycast’s potential applications for Android are vast. Beyond simple video streaming, we can expect Anycast to power personalized content delivery tailored to individual user preferences. Imagine a system that dynamically adjusts video quality based on your network conditions, offering optimal viewing experiences regardless of your location or connection strength. This adaptive approach is crucial for improving the accessibility and usability of high-bandwidth content on Android.
Potential Impact of Anycast on the Future of Mobile Computing
Anycast’s impact on mobile computing will be profound. It will potentially redefine how we consume information and access services, breaking down geographical barriers and enhancing global connectivity. We can anticipate a future where mobile devices become more powerful and versatile, seamlessly accessing resources from anywhere in the world.
Future Directions for Anycast in the Mobile Space, Focusing on Android
- Enhanced Content Delivery: Dynamically adjusting content quality and delivery based on real-time network conditions and user preferences will ensure a consistent and high-quality user experience, even in challenging environments. Consider streaming high-resolution videos while traveling on a weak Wi-Fi connection.
- Personalized Content Experiences: Anycast can personalize content delivery based on individual user profiles and preferences, delivering relevant and engaging information tailored to each user. This could involve adapting content based on location, time of day, or even user activity patterns.
- Improved Gaming Experiences: Anycast will potentially optimize gaming experiences by dynamically routing game data to the nearest and most capable server, reducing latency and improving overall performance. Think of seamless online multiplayer gaming, regardless of your physical location.
- Universal Access to Resources: Anycast will potentially unlock seamless access to resources across different geographical locations. This could include access to cloud services, educational materials, or even medical data, facilitating global connectivity.
