With VNC remote access IoT firewall free android, unlocking a world of possibilities is now within reach. Imagine effortlessly controlling your smart home appliances, industrial sensors, and other IoT devices from anywhere, anytime. This comprehensive guide dives into the fascinating realm of VNC, exploring its integration with IoT, security considerations, and the practicalities of using it on Android devices.
We’ll explore the ins and outs of firewalls, and delve into the benefits of free VNC solutions, providing a comprehensive toolkit for anyone looking to leverage this powerful technology.
VNC remote access, a technology that’s been around for a while, has found a new lease on life with the rise of IoT devices. Connecting to these devices remotely, for monitoring and control, opens up a myriad of opportunities. From home automation to industrial monitoring, the potential applications are vast. However, security remains paramount. Proper firewall configurations and strong authentication are critical to ensure the safety of your systems.
This guide will explore the crucial steps to secure your VNC connections and safeguard your IoT devices.
Introduction to VNC Remote Access: Vnc Remote Access Iot Firewall Free Android
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a powerful technology that allows you to remotely control a computer, or a specific application, from another device. Imagine accessing your home computer from a coffee shop, or controlling a server in a different building. VNC makes this kind of remote access a reality, simplifying tasks and boosting efficiency.VNC works by creating a virtual window on your remote computer, displayed on your local device.
You can interact with this virtual window as if you were directly in front of the remote machine, controlling everything from mouse clicks and keyboard inputs to opening programs and files. This technology transcends geographical limitations, making it a crucial tool for IT professionals, students, and even casual users.
Fundamental Concepts and Functionalities of VNC
VNC leverages a client-server architecture. A VNC client, running on your local machine, connects to a VNC server, running on the remote computer. This connection allows for the transfer of graphical data, keyboard input, and mouse movements between the two devices. The server processes these interactions and presents them to the client. This enables users to manage remote systems effectively.
Historical Context and Evolution of VNC, Vnc remote access iot firewall free android
VNC’s history reflects the evolution of remote computing. Early forms of remote access were often complex and resource-intensive. VNC emerged as a more user-friendly and efficient solution, quickly gaining popularity due to its open-source nature and robust capabilities. This open-source model fostered community development and continuous improvement, leading to significant advancements over the years. The open-source nature of VNC allowed for extensive customization and improvements.
How VNC Works
VNC utilizes a proprietary protocol to establish a secure connection. This protocol compresses and transmits data between the client and server, ensuring efficiency and responsiveness, even over slow networks. The connection process involves authentication and authorization, safeguarding sensitive information. The key is in the secure transmission of information.
Comparison of VNC Versions
| Version | Key Features | Security Improvements |
|---|---|---|
| VNC 4 | Support for a variety of operating systems, basic graphical interaction, and robust protocol for data transmission. | Implemented basic authentication mechanisms for initial connection security. |
| VNC 5 | Improved performance and enhanced security, supporting a broader range of devices and network environments, with greater stability and reliability. | Integrated stronger encryption methods, including the use of TLS, to protect data transmitted over the network. This provides a more secure connection. |
IoT Devices and VNC Integration

Unlocking the potential of your IoT devices just got easier. VNC remote access opens a gateway to managing and monitoring your connected world, from smart homes to industrial sensors. This integration streamlines control and troubleshooting, providing a comprehensive view of your network’s pulse.
VNC Integration with IoT Devices
VNC, or Virtual Network Computing, provides a powerful remote desktop protocol. Integrating it with IoT devices allows for remote control and monitoring, overcoming geographical limitations. This remote access is crucial for troubleshooting and maintenance, allowing technicians to diagnose issues and perform adjustments without physically being present.
Use Cases for VNC in IoT Management
VNC’s utility extends beyond basic remote access. It empowers efficient management of IoT devices, facilitating quick fixes and updates. For example, a technician can remotely diagnose a malfunctioning smart thermostat, adjust settings, or even update its firmware without leaving the office. Similarly, industrial sensors can be monitored and calibrated from a remote location, ensuring optimal performance and preventing downtime.
This remote access is crucial for proactive maintenance and streamlined operational efficiency.
Examples of VNC-Controlled IoT Devices
Numerous IoT devices benefit from VNC integration. A smart home system, for instance, can be remotely accessed and controlled via VNC. Imagine adjusting the temperature in your house or turning on the lights from anywhere in the world. Similarly, industrial sensors in a remote factory can be monitored and controlled remotely, enabling real-time data analysis and rapid responses to potential issues.
Furthermore, agricultural sensors can be accessed for monitoring crop conditions, enabling timely intervention and maximizing yield.
Challenges and Limitations of VNC with IoT
While VNC offers significant advantages, there are inherent challenges. Security concerns are paramount. Robust security protocols are crucial to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Moreover, the bandwidth required for smooth VNC sessions can be a limiting factor for some IoT devices, particularly those with limited connectivity. Additionally, the complexity of the device’s user interface can impact the usability of the VNC session.
Suitable IoT Devices for VNC Remote Access
The table below Artikels various IoT devices suitable for VNC remote access, considering typical specifications and compatibility. Careful consideration of device capabilities and VNC limitations is vital for successful integration.
| Device Type | Typical Specifications | VNC Compatibility |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Home Appliances (Thermostats, Lights, Locks) | Wi-Fi connectivity, embedded operating systems (e.g., Linux, embedded firmware) | Generally compatible, depending on manufacturer’s implementation and device specifications. Consider whether the device supports a remote desktop protocol or requires specific configuration. |
| Industrial Sensors (Temperature, Pressure, Flow) | Ethernet or wireless connectivity, data acquisition systems | Potential for compatibility, depending on the sensor’s communication protocol (e.g., Modbus, Profibus) and the ability to expose a remote access interface. Specific integration may require custom software. |
| Wearable Fitness Trackers | Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connectivity, limited processing power | Limited compatibility due to limited processing power and display capabilities. Remote access might be restricted to specific data retrieval rather than full device control. |
| Agricultural Sensors (Soil Moisture, Crop Health) | Wireless connectivity (e.g., LoRaWAN, Sigfox), data transmission | Compatibility is highly dependent on the sensor’s communication protocol and the remote access capabilities built into the system. Remote access might be limited to data retrieval. |
Security Considerations with VNC
Unlocking the power of remote access comes with a responsibility to secure it. VNC, while incredibly useful, presents potential security vulnerabilities if not handled with care. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate safeguards is crucial for protecting your IoT devices and sensitive data.Protecting your VNC access is paramount. A compromised VNC connection can expose your IoT devices to malicious actors, potentially leading to data breaches or unauthorized control.
This section dives into the security landscape of VNC, exploring the vulnerabilities and outlining effective countermeasures.
VNC Security Vulnerabilities
VNC, in its inherent nature as a remote access protocol, carries inherent risks if not properly configured. These vulnerabilities often stem from a lack of robust security measures or inadequate user awareness. Exploiting these vulnerabilities can lead to significant damage.
Potential Security Risks and Threats
Several potential security threats lurk when VNC is deployed without adequate safeguards. These risks include unauthorized access to devices, data breaches, and malicious code injection. A malicious actor could gain control of your IoT device, leading to disruptions or even more serious consequences.
Security Measures for Mitigating Risks
A proactive approach to security is key to safeguarding your VNC connections. Implementing strong security measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of a breach.
Importance of Strong Passwords and Authentication Protocols
Strong passwords and robust authentication are the first lines of defense against unauthorized access. Choose complex passwords, and consider implementing multi-factor authentication for added security. These measures are critical to protect your VNC access from unauthorized intrusions.
Security Best Practices for VNC Deployments
Implementing the following best practices can dramatically improve the security posture of your VNC deployments.
| Security Measure | Description | Implementation Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Passwords | Employ passwords with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid easily guessable words or personal information. | Use a password manager to generate and store complex passwords. Change passwords regularly. |
| Firewall Protection | Implement a firewall to block unauthorized access to your VNC server. Configure firewall rules to allow only legitimate connections. | Configure your firewall to block all incoming connections except those specifically allowed for VNC. Use a stateful firewall for enhanced security. |
| Regular Updates | Keep your VNC server and client software up-to-date with the latest security patches. Outdated software is a common entry point for attackers. | Establish a schedule for checking for updates and promptly installing them. |
| Network Segmentation | Isolate your VNC server from other network devices to limit the impact of a potential breach. | Create separate networks for VNC servers and other devices. |
| Access Control | Restrict access to your VNC server to authorized users only. Use user roles and permissions to limit access. | Use a role-based access control (RBAC) system to assign specific privileges to different users. |
VNC and Firewalls

VNC, or Virtual Network Computing, allows remote access to computers, but security is paramount. Firewalls are the gatekeepers of this access, ensuring only authorized connections are granted. Understanding how firewalls work with VNC is crucial for securing your remote access and protecting your IoT devices.Firewalls are essential components of network security. They act as a barrier between your internal network and the outside world, scrutinizing all incoming and outgoing traffic.
They are vital for controlling access to sensitive resources like VNC servers.
Firewall Roles in Securing VNC Connections
Firewalls play a critical role in regulating VNC traffic. They inspect every connection request, ensuring it adheres to predefined rules. This inspection process is a critical safeguard against unauthorized access attempts. Without proper firewall configuration, your VNC server becomes vulnerable to intrusion.
Firewall Configuration for VNC Traffic
Configuring firewalls for VNC access involves specifying which ports and protocols are allowed. This allows authorized users to connect while blocking unwanted connections. Careful configuration is key to balancing security and usability.
Different Firewall Types and their Impact on VNC
Various firewall types exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Packet filtering firewalls inspect individual packets, while stateful inspection firewalls track connections. The chosen type will impact the granularity of control over VNC traffic. For example, a packet filtering firewall might only allow connections on a specific port, while a stateful inspection firewall can monitor the entire session.
Comparing and Contrasting Firewall Configurations for VNC
Different firewall configurations for VNC access offer varying levels of security and control. A simple configuration might only allow connections on a specific port, while a more complex setup could involve multiple rules, IP address restrictions, and user authentication. The best configuration depends on the specific security needs and the complexity of the network.
Summary Table of Firewall Rules for VNC Access
| Firewall Rule | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Allow VNC port (e.g., port 5900) | Specifies that connections using the VNC protocol on port 5900 are permitted. | Allows authorized remote access to the VNC server. |
| Block VNC port (e.g., port 5900) | Specifies that connections using the VNC protocol on port 5900 are denied. | Prevents unauthorized access to the VNC server, enhancing security. |
| Allow VNC traffic from specific IP addresses | Only permits connections from particular IP addresses, potentially for a particular device or user. | Increases security by restricting access to trusted sources. |
| Block VNC traffic from specific IP addresses | Denies connections from specific IP addresses. | Helps prevent malicious attacks from known or suspected sources. |
| Require VNC authentication | Enforces authentication procedures (e.g., username/password) for all VNC connections. | Significantly enhances security by requiring user verification. |
VNC Remote Access on Android
Unlocking the potential of your IoT devices and network from your Android smartphone has never been easier with VNC. This powerful remote access technology allows you to seamlessly control and manage your connected devices, whether it’s a smart home system, a business network, or a personal project. This capability is especially valuable for troubleshooting, configuration, and real-time monitoring.VNC, or Virtual Network Computing, acts as a bridge, enabling your Android device to interact with other computers and devices over a network.
Think of it as a virtual pair of hands extending from your phone, allowing you to manipulate displays and control programs on the target device. This capability is highly beneficial for troubleshooting, configuration, and real-time monitoring.
Popular VNC Client Applications for Android
Several robust VNC client applications are readily available for Android devices. These apps offer varying features, including support for different VNC protocols, security options, and user interfaces. The choice of application depends on your specific needs and preferences. Key features to consider include stability, performance, and the security protocols employed.
Performance Considerations for VNC on Android
The performance of VNC on Android devices depends on several factors. These include the speed and stability of your network connection, the processing power of your Android device, and the complexity of the remote application or device. High-bandwidth connections, such as fiber optic or 5G networks, are generally preferable for smooth VNC sessions. Conversely, less powerful devices might struggle with resource-intensive applications or demanding graphical interfaces, resulting in slower or jerky responses.
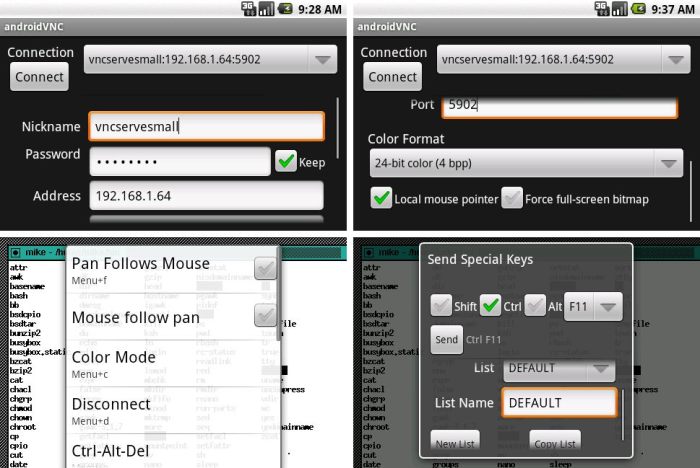
Configuring VNC on an Android Device for Remote Access
Proper configuration is essential for secure and reliable VNC access. This involves establishing a secure connection between your Android device and the target device. First, ensure that the VNC server is correctly configured on the remote device. Then, install the chosen VNC client application on your Android device. Finally, enter the IP address or hostname of the remote device and the necessary credentials to establish a connection.
Steps for Configuring VNC on an Android Device
- Ensure the VNC server is activated on the remote device. This involves configuring the server software on the target system, including setting up a specific port and enabling authentication.
- Download and install a VNC client application on your Android device from the Google Play Store. Reputable and widely-used apps often come with detailed instructions within their documentation or support pages.
- In the VNC client app, enter the IP address of the remote device and the designated port number for VNC access. Verify the correct information. Secure connections typically require a password or other authentication method.
- Provide the necessary credentials to establish a secure connection. The remote device’s security settings might require authentication with a password or other methods.
- Establish the connection, and you should now have remote access to the device.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Using VNC on Android
- What is the best VNC client for Android? The “best” VNC client is subjective and depends on your specific needs and preferences. Consider factors such as features, performance, user interface, and security protocols.
- How can I improve VNC performance on Android? Optimizing network conditions and device resources is crucial. A stable, high-bandwidth connection and a device with sufficient processing power can significantly improve performance.
- Are there any security concerns with using VNC on Android? Yes, using VNC necessitates a secure connection. Verify the VNC server’s security configurations, employ strong passwords, and ensure the VNC client application is from a reputable source to mitigate potential risks.
- Can I use VNC to access devices on a different network? Yes, but network connectivity must be established between the devices.
Free VNC Solutions
Unlocking remote access to your IoT devices doesn’t have to break the bank. Plenty of fantastic, free VNC solutions are available, offering a robust and reliable way to connect and control your devices without hefty price tags. These options often come with a rich set of features, though their capabilities might differ slightly from their paid counterparts.Exploring these free choices allows you to connect with your devices efficiently, saving you money while ensuring smooth operations.
This section will guide you through the world of free VNC solutions, highlighting their advantages and drawbacks, and showcasing some popular options.
Open-Source and Free VNC Clients
Free VNC solutions are often open-source, meaning the software’s code is publicly available. This transparency fosters collaboration and allows users to contribute to its improvement. This collaborative environment leads to a more robust and adaptable solution over time. Many free VNC clients offer comparable functionalities to their commercial counterparts, making them a viable option for various needs.
Benefits and Limitations of Free VNC Solutions
Free VNC solutions often come with significant advantages. Their cost-effectiveness is a major draw, allowing users to access remote access tools without incurring any licensing fees. The inherent transparency of open-source solutions can foster trust and confidence in their reliability and security. However, free solutions might have some limitations. Features might be slightly less comprehensive than paid options, and support for less common devices or platforms might be less extensive.
Performance could also be influenced by server resources and bandwidth, as opposed to solutions specifically optimized for high-performance applications.
Examples of Free VNC Software
Several excellent free VNC clients are available across different operating systems. They offer a diverse range of capabilities and functionalities to cater to various needs.
- RealVNC: A widely recognized open-source VNC solution that’s compatible with a variety of platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and Android. Its broad platform support and ease of use make it a popular choice for diverse user needs.
- TightVNC: Another powerful and versatile open-source VNC client. Known for its performance and extensive feature set, TightVNC is particularly well-suited for users seeking a reliable and high-performing solution for various applications.
- VNC Viewer: A popular choice for Windows users. It is a simple yet effective VNC client, often a good starting point for individuals wanting a straightforward way to connect to remote devices.
Comparison Table of Free VNC Clients
This table provides a concise comparison of various free VNC clients, highlighting their platform compatibility, key features, advantages, and disadvantages.
| Client | Platform | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RealVNC | Windows, macOS, Linux, Android | High compatibility, ease of use, broad feature set | Versatile, cost-effective, open-source | Might have slight performance limitations compared to paid alternatives in some scenarios |
| TightVNC | Windows, macOS, Linux | High performance, extensive feature set, customizable | Reliable, high-performance, open-source | Steeper learning curve compared to RealVNC for some users |
| VNC Viewer (Free) | Windows | Simple, user-friendly interface, basic functionalities | Easy to use, cost-effective | Limited features compared to RealVNC or TightVNC |
